Welcome to the second tutorial on networks for hackers. We are going to learn network types and weaknesses and strengths of networks in this tutorial.
You can read the first tutorial if you don’t have any information about networks. We are using some terms found in the first article in this tutorial.
This article includes LAN (Local Area Networks), PAN(Personal Area Network), MAN(Metropolitan Area Network), WAN(Wide Area Network).
You will also learn LAN topologies, advantages and disadvantages of network types, and network security issues in this article.
Network Types
We learned network terms and private-public networks. They are classified according to the size of the collection of interconnected devices.
The 4 types that will be covered in this article are grouped according to their size, for example, LAN is the smallest network group and WAN is the largest network group.
The size of a network determines according to the number of devices communicating on the network.
Routers and Switchers
Before learning network types we need to learn these terms for understanding network hierarchy.
Switchers are used to collecting more than one device at a single point and connecting them to the internet or a different main device.
Routers are used to interconnect networks and transfer data to other devices or networks.
The router can connect switches, enable communication between switches. Thus, you can combine devices with switchers and connect switchers with routers to communicate between switchers.
1 – LAN (Local Area Network)
A local network is a small network system that communicates with computers through hardware such as ethernet cables and hubs.
Local networks can have switchers and routers. Computers can communicate from a single point via switchers instead of ethernet cables.
There are different types of LANs, thanks to different ways of connecting, different routers, and different topologies.
Star Topology
There is switches or hub in the middle, in this topology, the central network device connects the devices separately and provides communication.
Data (packet) is sent from the central device. After that switch, send the data to the device that the data needs to reach.
Disadvantages: The need for more cables and devices. If there is a malfunction in the central device, the communication is completely cut off.
Advantages: Cases such as collapse are rare. It is suitable for big data exchanges. It’s easier to scale devices.
Ring Topology
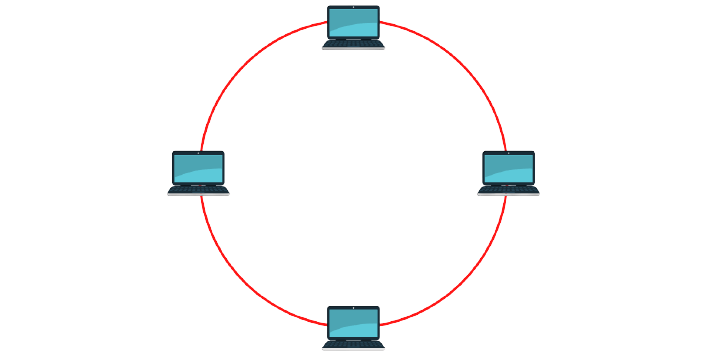
It is a topology that allows devices such as computers to be connected to each other in a loop with the help of a very little cable.
Ring topology relies on translating data in the loop until data reaches the targeted device, using other devices throughout the loop to transmit data.
The ring topology is easy to maintain and repair, however, one of its major drawbacks is that it can bottleneck large systems.
The ring topology is easy to maintain and repair, but one of its major drawbacks is that if a link between two computers breaks, all communication is lost.
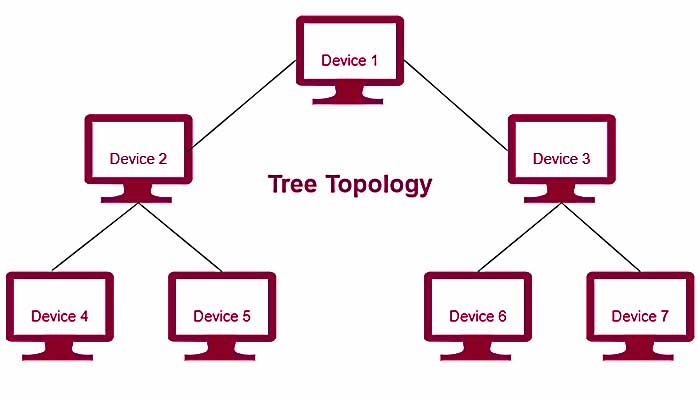
Tree Topology
Tree topology is a hierarchical network topology, the top device is connected to the bottom device in stages.
In the tree topology, the first device is connected to 2 devices, then this number increases to 4, and so on. The number of the connected devices may vary
Tree topology is similar to a star topology, each node is connected to a hub, but only a few nodes are directly connected to the central hub.
Advantages: It provides high scalability, It provides easy maintenance and fault identification. Other nodes in a network are not affected if one of their nodes gets damaged.
Disadvantages: On the failure of a hub, the entire network fails. Large cabling is required as compared to star and bus topology.
Bus Topology
This type of connection consists of many devices connected to the backbone cable, when your backbone cable is damaged your network shutdown.
Since the data targeted for each device passes through the common cable, the bottleneck risk is higher than other topologies.
Bus topology is more economical than other topologies. However, it comes with many disadvantages.
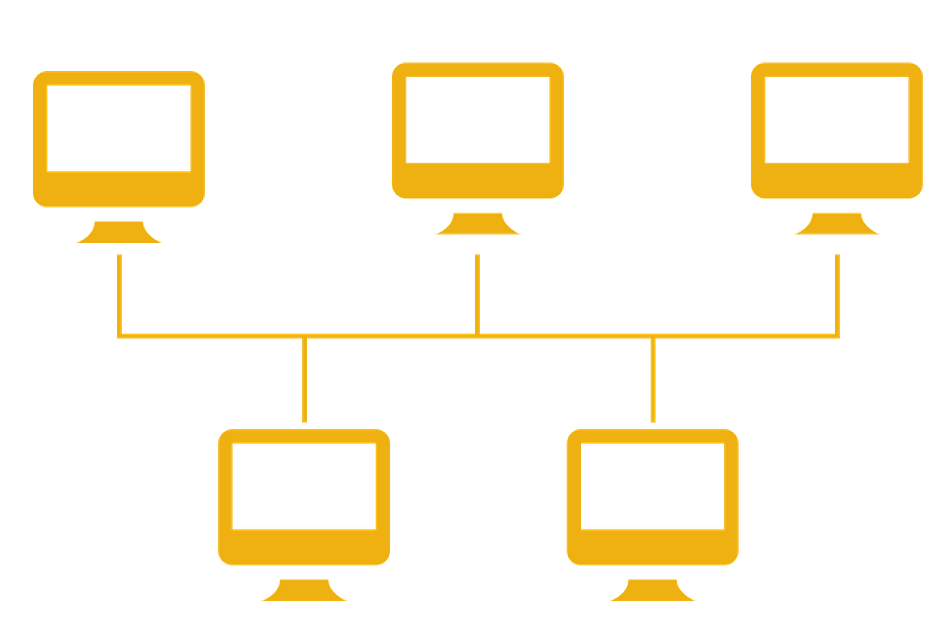
Advantages: It works efficiently with a small network, adding new devices in this topology easier than other topologies, this solution cheaper.
Disadvantages: Fixing bugs is very difficult (believe me, very difficult), the performance of bus topology in large networks is terrible.
2 – PAN (Personal Area Network)
You can think of it as a scaled-down and slower data transfer version of Local Area Network, and Personal Area Network can be thought of as a subset of LAN.
The size of a Personal Network can be several centimeters or several meters. PANs can be networked (Bluetooth and WIFI) or wired (USB, FireWire).
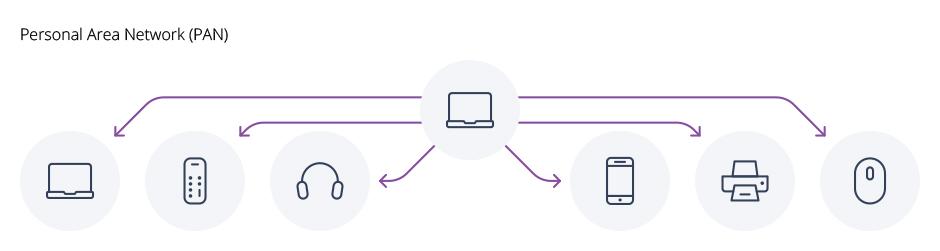
Devices in the PAN can exchange data with each other. Personal Area Network usually does not have a router, so it cannot connect directly to the Internet.
Headphones or keyboards etc. with a Bluetooth connection, while your computer connects to the Internet, while others do not, but can connect to your computer.
What is WPAN?
A wireless personal area network, as the name suggests, is a group of devices where there is no physical connection.
Bluetooth is generally used to connect devices in WPAN systems, it can be observed that WLAN is used occasionally (There are other alternatives).
WPAN’s range is often very small, as short-range wireless such as Bluetooth is not efficient over distances greater than 5-10 meters.
3 – MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
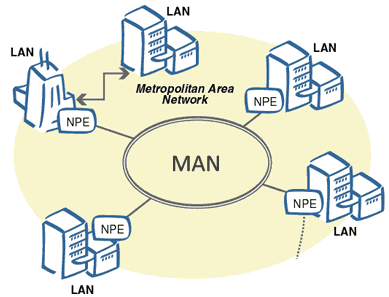
You may have deduced the following meaning from its name, is this network only used in metropolitan cities? No, Its name indicates its size, not its area of use.
Networks larger than the Local Network Area are called MAN, more than one LAN or PAN can be added to the Metropolitan Network Area.
Fiber optic cable is used to connect LANs. These fiber optic cables may be leased from private-sector Internet service providers (ISP).
The type of network that connects school or campus buildings is called CAN. In these networks, it can be included in MAN.
Advantages: MAN lets you centrally manage many LAN communications, creating MAN is pretty easy. The security level is high.
Disadvantages: If MAN increases in size, it becomes more difficult to manage (security issues, etc.). Highly secure personnel are essential for MANs.
4 – WAN (Wide Area Network)

The largest network under current conditions is called WAN. a WAN is a collection of local-area networks or other networks that communicate with one another.
The first wide area network was established by the US Air Force in the late 1950s to interconnect sites in the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment radar defense system.
Examples of WANs used in daily life: Internet, US Department of Defense, Banks, Airlines, and Satellite systems
One of the ways organizations connect their LANs to form a WAN is to use called a leased line. A leased line is a large network connection leased by ISS.
To create a WAN you need to combine LAN and MAN networks, data is transmitted through hubs, switches, modems, and fiber optic cables.
Advantages: It provides data transmission even to very remote areas, provides high bandwidth (data transmission rate), allows you to distribute the workload.
Disadvantages: More security issues than MAN and LAN, higher installation cost (too much), hard to correct errors due to their size.